| Title | Numerical methods for direct scattering problems | ||||||||||||||||||
| Participant | Klaus Giebermann | ||||||||||||||||||
| Key words | scattering theory, integral equations, Helmholtz equation, Lippmann-Schwinger integral equation | ||||||||||||||||||
| Description |
This project concerns with the numerical solution of scattering
problems in 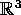 .
The aim of this project is the numerical simulation of the scattering
of acoustic and electromagnetic waves in .
The aim of this project is the numerical simulation of the scattering
of acoustic and electromagnetic waves in 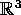 .
Given an incomming wave ui and an obstacle .
Given an incomming wave ui and an obstacle
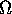 we are interested in the
scattered wave us. Under the additional assuption that the
incomming wave is time-harmonic, the problem can be formulated as
a boundary value problem for the Helmholtz-equation in an unbounded domain.
One way to solve this boundary value problem is to reformulate it to
a boundary integral equation. This equation can then be discretized by
the boundary element method (BEM). we are interested in the
scattered wave us. Under the additional assuption that the
incomming wave is time-harmonic, the problem can be formulated as
a boundary value problem for the Helmholtz-equation in an unbounded domain.
One way to solve this boundary value problem is to reformulate it to
a boundary integral equation. This equation can then be discretized by
the boundary element method (BEM).
Time harmonic scatteringThe assumption that the incomming wave ui is time-harmonic implies that the scattered wave is time-harmonic, too. Therefore, we can represent each wave U(x,t) in the following manner:
Examples
Sound-hard obstacle
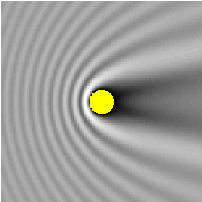
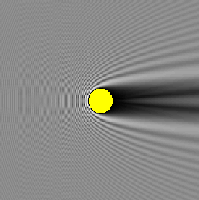
Scattering in homogeneous mediaThe scatterig of a time-harmonic acoustic wave ui leads to boundary value problem for Helmholtz-equation
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Bibliography |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Related projects |